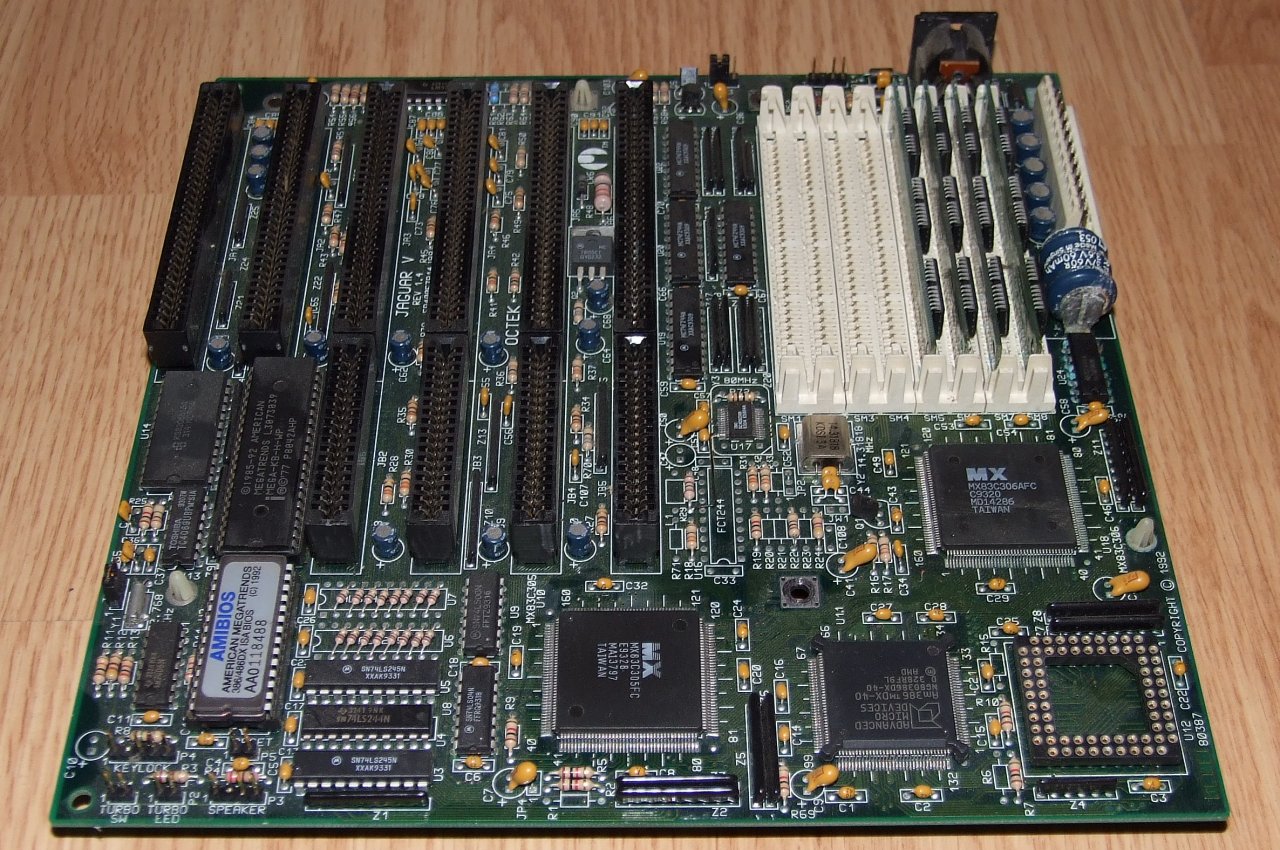
The Octek Jaguar V motherboard from 1993. This board has 6 ISA slots but few onboard peripherals, as evidenced by the lack of external connectors.
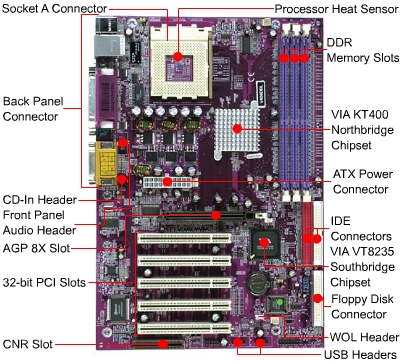
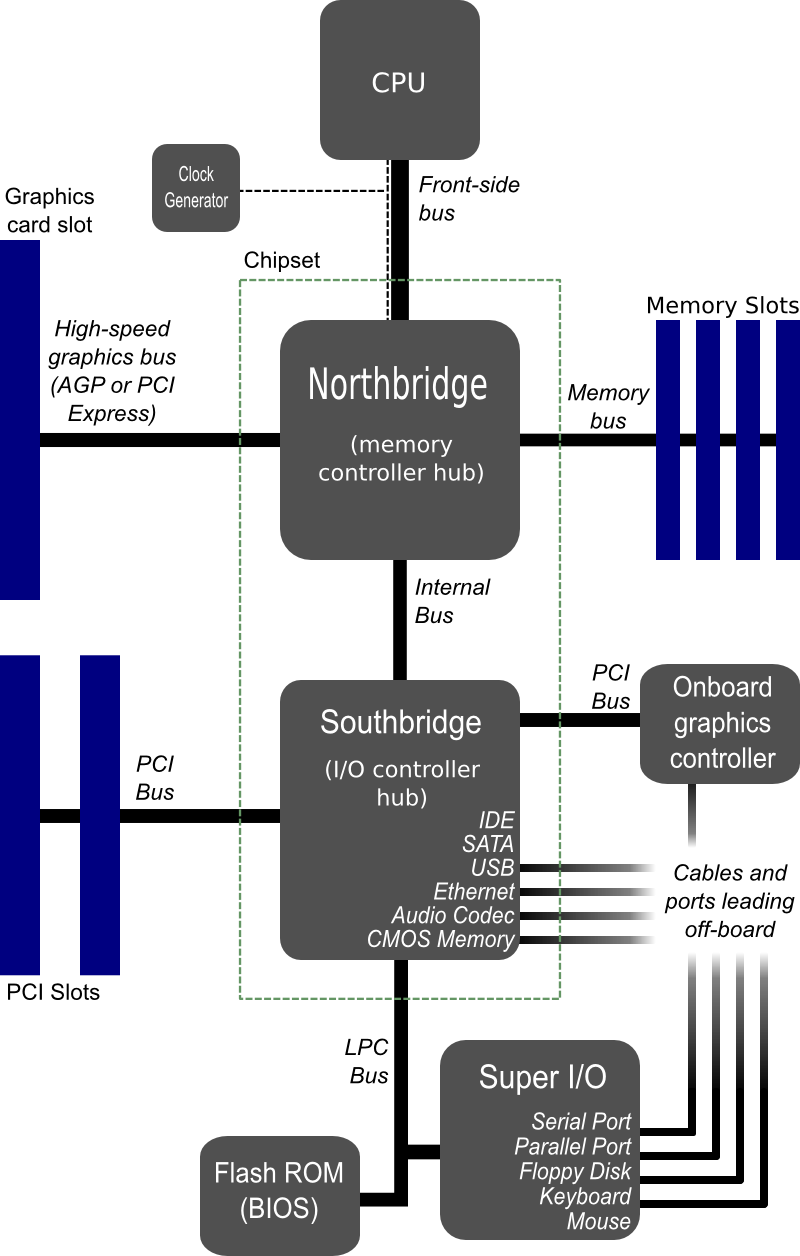
Diagram of a modern motherboard, which supports many on-board peripheral functions as well as several expansion slots.
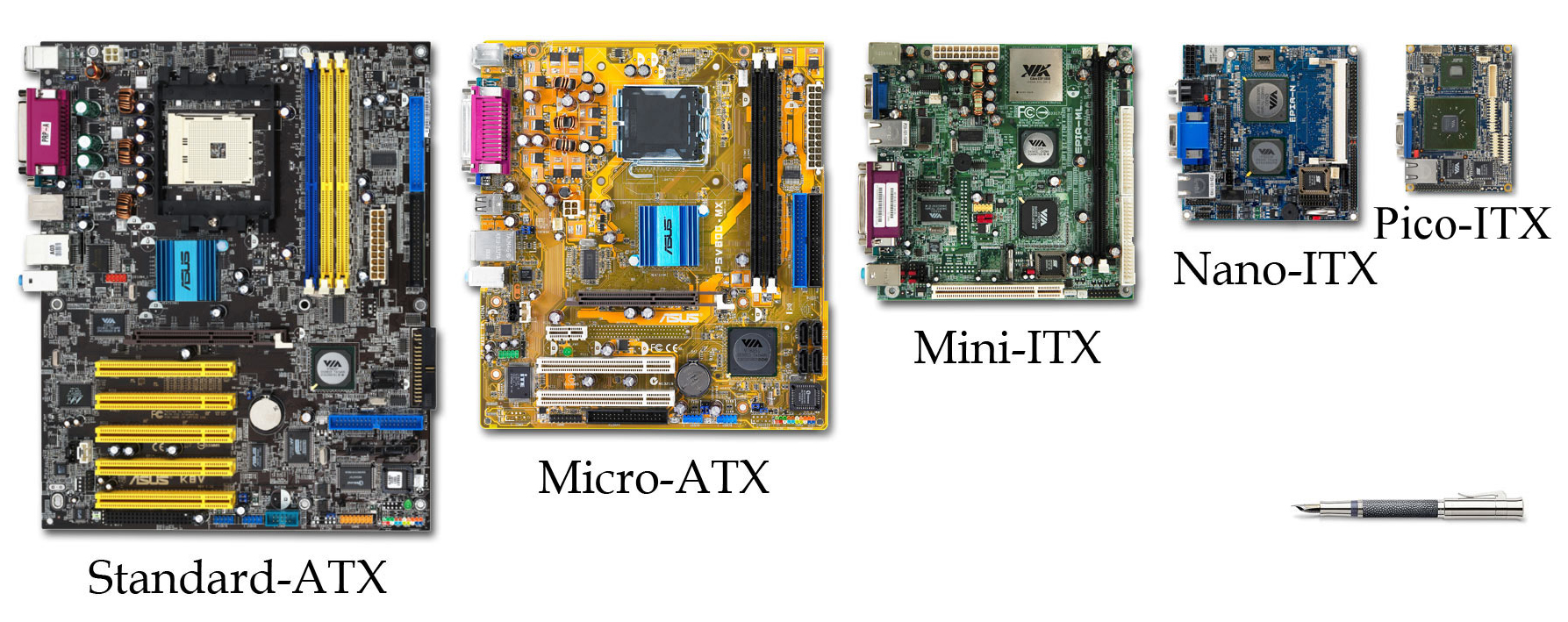
As new generations of components
have been developed, the standards of motherboards have changed too - for
example with AGP
being introduced, and more recently PCI Express.
However the basic standardized size and layout of motherboard have changed much
more slowly, and are controlled by their own standards. This is helped by the
fact that in many ways, the list of components a motherboard must include
changes far slower than the components themselves. For example, north bridge controllers have changed many
times since their original introduction, with many manufacturers bringing out
their own versions, but in terms of form factor standards, the requirement to
allow for a north bridge has remained fairly static for many years.
References..Wikipedia